It's a return to what worked before
- Written by Steven Hail, Lecturer in Economics, University of Adelaide

It’s easy get the impression the massive government spending and deficits and debt required by the pandemic are new.
It would be understandable, because much of what happened before the 1980s has been forgotten.
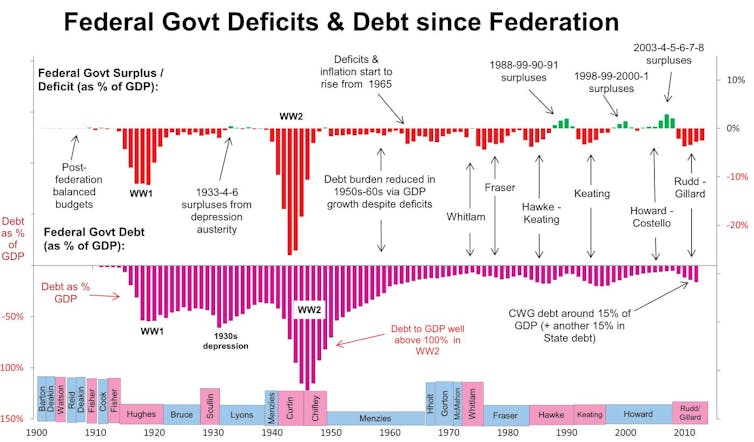
Yet for almost all of the years since Federation – almost every one – the Commonwealth budget has been in deficit, right through til the late 1980s.
And it has hurt us not at all.
 Centric Wealth[1] Seventy five years ago, the world faced daunting challenges: the reconstruction of Europe and Japan; the long-overdue end of an empire; the threat of communism; urgent demands for public services, social welfare and housing; and the orientation of economic activity away from the demands of war towards improvements in the quality of life.
Centric Wealth[1] Seventy five years ago, the world faced daunting challenges: the reconstruction of Europe and Japan; the long-overdue end of an empire; the threat of communism; urgent demands for public services, social welfare and housing; and the orientation of economic activity away from the demands of war towards improvements in the quality of life.  The Argus, May 31 1945. NLA Trove[2] In Australia, the Commonwealth published a white paper, Full Employment in Australia,[3] in which it accepted responsibility for ensuring that there would always be enough demand for labour so that everyone who wanted to a job would be able to get one. In pursuit of this goal, both sides of politics understood that they would usually need to run budget deficits. For 40 years under prime ministers Chifley, Menzies, Holt, Gorton, McMahon, Whitlam and Fraser that is exactly what happened, as it had for most of the 40 previous years without the guiding light of the white paper. Governments would spend as much as was needed (some of it in the form of gigantic nation-building projects such as the Snowy Mountains Scheme[4]) and tax as little as was needed in order to keep the unemployment rate at close to zero as practical without putting too much pressure on prices. If there were deficits, low interest rates and the economic growth that flowed from those deficits would shrink the resulting debt as a proportion of GDP. Banks were regulated to ensure interest rates stayed low and credit was directed to businesses and households. Menzies was a Keynesian These were the golden years of so-called Keynesian economics[5] with a consensus across the political spectrum that it was right to use government spending and tax measures to sustain the economy, disputed only by Marxists on the Left and a small band of neoliberals on the Right. Up until the mid-1970s, when war in the Middle East, fautrising energy prices in a world dependent on oil and rising union militancy in Australia combined to create double-digit inflation and an unemployment rate far higher than the one or two per cent Australia had enjoyed since the war. Read more: Memories. In 1961 Labor promised to boost the deficit to fight unemployment. The promise won[6] In Australia and elsewhere it allowed a takeover by a new band of neoliberal[7] politicians and economists who believed in small government (sometimes austerity), balanced budgets and outsourcing economic management to central banks who were given the autonomy to adjust interest rates and the supply of money in a deregulated market. It happened slowly, under the governments of Margaret Thatcher in the United Kingdom, Ronald Reagan in the United States and (Labor prime minister) Bob Hawke in Australia. Hawke was an exception By the 1990s, the old consensus had not only disappeared, its successes had been erased from memories. A new academic and institutional consensus emerged, shared by prime ministers Hawke, Keating and Howard and treasurers Keating and Costello. Although it does not require balanced budgets, the Charter of Budget Honesty[8] introduced by Treasurer Peter Costello requires governments to publish the fiscal strategy[9] they intend to use in drawing up budgets. Read more: Frydenberg is setting his budget ambition dangerously low[10] The first, in 1997[11] required the government to achieve “underlying budget balance, on average, over the course of the economic cycle”. Over time it was hardened to “achieve budget surpluses, on average, over the course of the economic cycle”.
The Argus, May 31 1945. NLA Trove[2] In Australia, the Commonwealth published a white paper, Full Employment in Australia,[3] in which it accepted responsibility for ensuring that there would always be enough demand for labour so that everyone who wanted to a job would be able to get one. In pursuit of this goal, both sides of politics understood that they would usually need to run budget deficits. For 40 years under prime ministers Chifley, Menzies, Holt, Gorton, McMahon, Whitlam and Fraser that is exactly what happened, as it had for most of the 40 previous years without the guiding light of the white paper. Governments would spend as much as was needed (some of it in the form of gigantic nation-building projects such as the Snowy Mountains Scheme[4]) and tax as little as was needed in order to keep the unemployment rate at close to zero as practical without putting too much pressure on prices. If there were deficits, low interest rates and the economic growth that flowed from those deficits would shrink the resulting debt as a proportion of GDP. Banks were regulated to ensure interest rates stayed low and credit was directed to businesses and households. Menzies was a Keynesian These were the golden years of so-called Keynesian economics[5] with a consensus across the political spectrum that it was right to use government spending and tax measures to sustain the economy, disputed only by Marxists on the Left and a small band of neoliberals on the Right. Up until the mid-1970s, when war in the Middle East, fautrising energy prices in a world dependent on oil and rising union militancy in Australia combined to create double-digit inflation and an unemployment rate far higher than the one or two per cent Australia had enjoyed since the war. Read more: Memories. In 1961 Labor promised to boost the deficit to fight unemployment. The promise won[6] In Australia and elsewhere it allowed a takeover by a new band of neoliberal[7] politicians and economists who believed in small government (sometimes austerity), balanced budgets and outsourcing economic management to central banks who were given the autonomy to adjust interest rates and the supply of money in a deregulated market. It happened slowly, under the governments of Margaret Thatcher in the United Kingdom, Ronald Reagan in the United States and (Labor prime minister) Bob Hawke in Australia. Hawke was an exception By the 1990s, the old consensus had not only disappeared, its successes had been erased from memories. A new academic and institutional consensus emerged, shared by prime ministers Hawke, Keating and Howard and treasurers Keating and Costello. Although it does not require balanced budgets, the Charter of Budget Honesty[8] introduced by Treasurer Peter Costello requires governments to publish the fiscal strategy[9] they intend to use in drawing up budgets. Read more: Frydenberg is setting his budget ambition dangerously low[10] The first, in 1997[11] required the government to achieve “underlying budget balance, on average, over the course of the economic cycle”. Over time it was hardened to “achieve budget surpluses, on average, over the course of the economic cycle”. 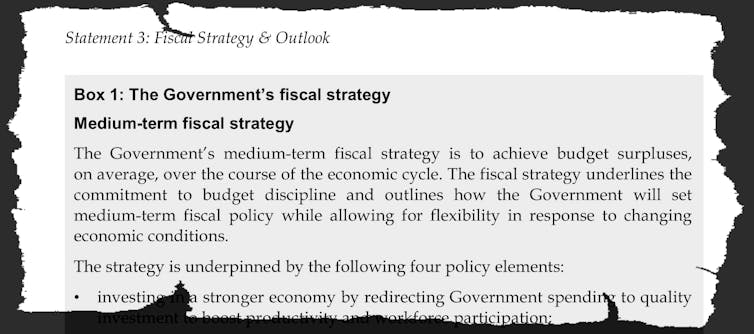 Commonwealth budget, 2019-20[12] It has been honoured in the breach since 2008, because surpluses usually aren’t consistent with good economic management, regardless of charters. If the private sector is a net saver, as it usually is, the public sector usually needs to be a net spender in order to keep resources fully employed. In last year’s election Prime Minister Scott Morrison and his opponent Bill Shorten disagreed about many things, but the need for surpluses wasn’t one of them Surpluses no longer No longer. In the leadup to tomorrow’s budget Treasurer Josh Frydenberg has promised a new fiscal strategy[13], one that for the first time is likely to promise neither a surplus or a balanced budget. “It would now be damaging to the economy and unrealistic to target surpluses over the forward estimates, he said in September. "This would risk undermining the economic recovery we need to bring hundreds of thousands more Australians back to work and to underpin a stronger medium-term fiscal position”. Proponents of the neoliberal consensus would argue that the decade of surpluses between the late 1990s and the global financial crisis was a golden time. It was certainly helped by the mining boom. Read more: Bernie Sanders' economic adviser has a message for Australia we might just need[14] But inequality grew[15], household debt trebled, and as the government continued to target a surplus, interest rates had to be cut to the point where further cuts may no longer have an effect[16]. Inflation has been below the Reserve Bank’s target and unemployment above it for a decade. The budget is about all that’s left to support the economy. It certainly shouldn’t be getting out of the way to allow the private sector to create wealth, as those proponents used to suggest[17]. We are on the cusp or a second Keynesian revolution, one expression of which is Modern Monetary Theory[18], which suggests deficits need to be embraced where they are necessary to bring about full employment. A government such as Australia’s which issues its own currency is able to fund deficits for as long as it needs to, and would be wise to do so up until the point where it creates too much inflation. Something stronger With the package comes the idea of a job guarantee, first put forward by the American economist Hyman Minsky in the 1960s, and promoted now by University of Newcastle labour market specialist Bill Mitchell[19] and the founder of the Cape York Institute Noel Pearson[20]. It is the unconditional offer of a job at a minimum wage to anyone willing and able to work, normally funded by budget deficits and bigger when the economy is weak and smaller when it is strong. Will it happen? As Stephanie Kelton, the world’s most prominent Modern Monetary Theorist and author of the New York Times bestseller The Deficit Myth[21] said recently, “I won’t say no. But it’s going to be a hell of a fight[22].
Commonwealth budget, 2019-20[12] It has been honoured in the breach since 2008, because surpluses usually aren’t consistent with good economic management, regardless of charters. If the private sector is a net saver, as it usually is, the public sector usually needs to be a net spender in order to keep resources fully employed. In last year’s election Prime Minister Scott Morrison and his opponent Bill Shorten disagreed about many things, but the need for surpluses wasn’t one of them Surpluses no longer No longer. In the leadup to tomorrow’s budget Treasurer Josh Frydenberg has promised a new fiscal strategy[13], one that for the first time is likely to promise neither a surplus or a balanced budget. “It would now be damaging to the economy and unrealistic to target surpluses over the forward estimates, he said in September. "This would risk undermining the economic recovery we need to bring hundreds of thousands more Australians back to work and to underpin a stronger medium-term fiscal position”. Proponents of the neoliberal consensus would argue that the decade of surpluses between the late 1990s and the global financial crisis was a golden time. It was certainly helped by the mining boom. Read more: Bernie Sanders' economic adviser has a message for Australia we might just need[14] But inequality grew[15], household debt trebled, and as the government continued to target a surplus, interest rates had to be cut to the point where further cuts may no longer have an effect[16]. Inflation has been below the Reserve Bank’s target and unemployment above it for a decade. The budget is about all that’s left to support the economy. It certainly shouldn’t be getting out of the way to allow the private sector to create wealth, as those proponents used to suggest[17]. We are on the cusp or a second Keynesian revolution, one expression of which is Modern Monetary Theory[18], which suggests deficits need to be embraced where they are necessary to bring about full employment. A government such as Australia’s which issues its own currency is able to fund deficits for as long as it needs to, and would be wise to do so up until the point where it creates too much inflation. Something stronger With the package comes the idea of a job guarantee, first put forward by the American economist Hyman Minsky in the 1960s, and promoted now by University of Newcastle labour market specialist Bill Mitchell[19] and the founder of the Cape York Institute Noel Pearson[20]. It is the unconditional offer of a job at a minimum wage to anyone willing and able to work, normally funded by budget deficits and bigger when the economy is weak and smaller when it is strong. Will it happen? As Stephanie Kelton, the world’s most prominent Modern Monetary Theorist and author of the New York Times bestseller The Deficit Myth[21] said recently, “I won’t say no. But it’s going to be a hell of a fight[22]. References
- ^ Centric Wealth (assets.documentcloud.org)
- ^ NLA Trove (trove.nla.gov.au)
- ^ Full Employment in Australia, (www.billmitchell.org)
- ^ Snowy Mountains Scheme (www.environment.gov.au)
- ^ Keynesian economics (www.investopedia.com)
- ^ Memories. In 1961 Labor promised to boost the deficit to fight unemployment. The promise won (theconversation.com)
- ^ neoliberal (www.investopedia.com)
- ^ Charter of Budget Honesty (cdn.theconversation.com)
- ^ fiscal strategy (budget.gov.au)
- ^ Frydenberg is setting his budget ambition dangerously low (theconversation.com)
- ^ 1997 (archive.budget.gov.au)
- ^ Commonwealth budget, 2019-20 (budget.gov.au)
- ^ new fiscal strategy (ministers.treasury.gov.au)
- ^ Bernie Sanders' economic adviser has a message for Australia we might just need (theconversation.com)
- ^ inequality grew (www.acoss.org.au)
- ^ no longer have an effect (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ used to suggest (www.economicshelp.org)
- ^ Modern Monetary Theory (theconversation.com)
- ^ Bill Mitchell (bilbo.economicoutlook.net)
- ^ Noel Pearson (www.theaustralian.com.au)
- ^ The Deficit Myth (blogs.lse.ac.uk)
- ^ hell of a fight (findingmoneyfilm.com)
Authors: Steven Hail, Lecturer in Economics, University of Adelaide
Read more https://theconversation.com/big-budget-spending-isnt-new-its-a-return-to-what-worked-before-142370













